アルツハイマー病の原因は、アミロイドβと呼ばれるタンパク質
断片が脳に蓄積することですが、この根幹となる病態に有効な治療
法は未だ開発されていません。
分子神経科学研究センターの研究グループは、アミロイドβの脳
内産生を抑えるタンパク質ILEIを新たに同定しました。健常者に比
してアルツハイマー病患者の脳ではILEIの発現が減少している一
方、アルツハイマー病モデルマウスの脳にILEIを強制的に発現させ
ることにより、発症が抑制されることを確認しました(グラフC)。こ
れまで、セクレターゼとよばれるタンパク質分解酵素の活性阻害剤
がアミロイドβ産生を抑制する薬剤として開発されていましたが、
副作用のため臨床応用は阻まれています。ILEIはセクレターゼ活
性を阻害することなくアミロイドβ産生を減らしアルツハイマー病
の発症を抑制することから、ILEIが予防法や治療法の開発に新た
な境地を開くことが期待されます。
Accumulation of Aβ in the brain underlies the pathogenesis of AD.
Although γ-secretase is a major target for therapeutic reduction of
Aβ production, non-selective inhibition of its activity causes serious
adverse effects due to blockade of Notch signaling. We identified
a secretory protein named ILEI as a negative regulator of Aβ
production. Notch signaling andγ-secretase activity are not affected
by ILEI. We also show neuronal expression of ILEI and marked
decrease in the level of secreted ILEI in AD brains. Transgenic
overexpression of ILEI significantly reduces the brain Aβ burden and
ameliorates the memory deficit in AD model mice. ILEI may be a
plausible target for the development of disease-modifying therapies.
(Nature Communications 5:3917, 2014)
●新たな抗アミロイドβ治療法の開発
New Strategy of Anti-amyloid-β (Aβ) Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
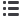
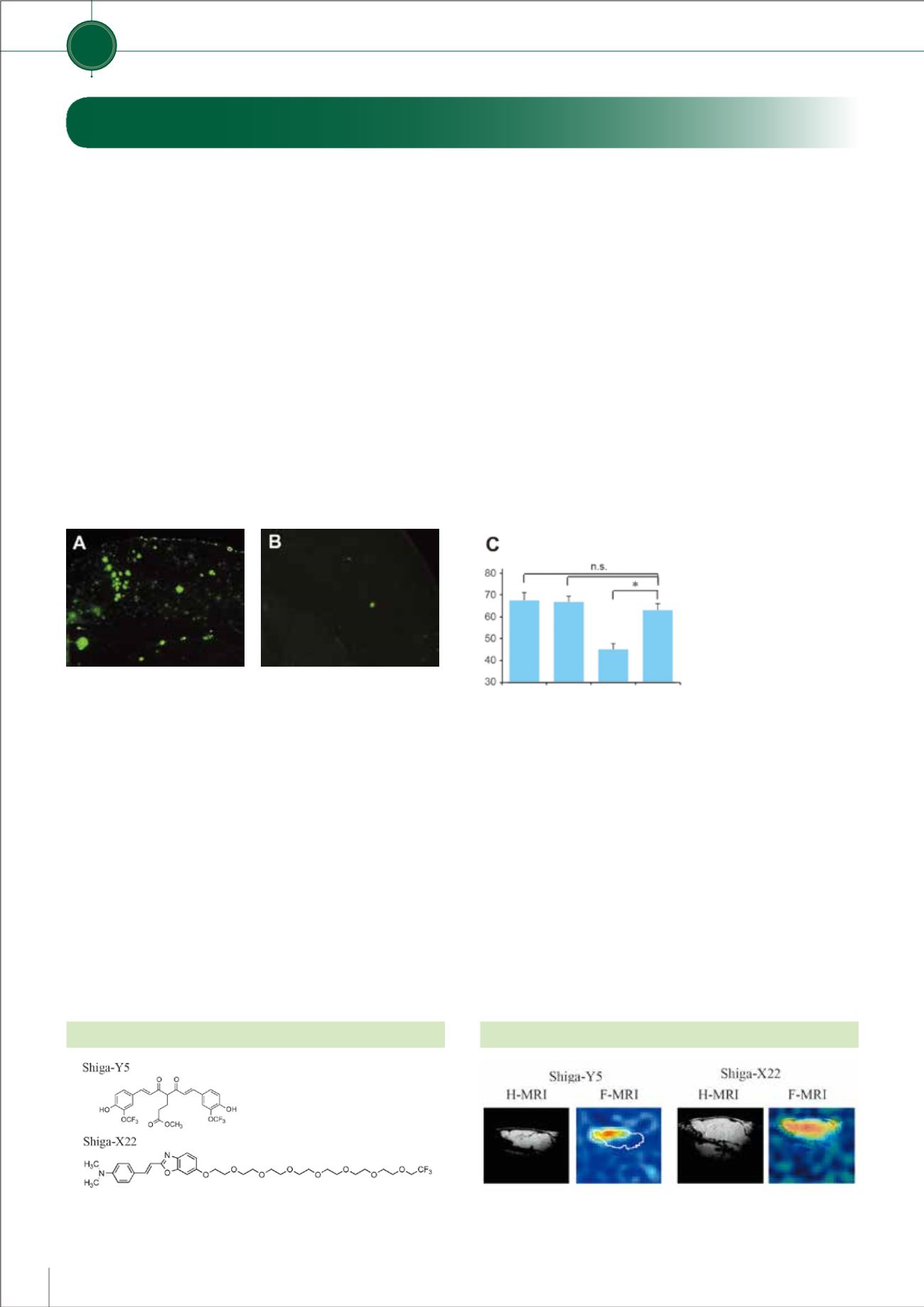
モデルマウスの脳ではAβ沈着が斑状(緑の蛍光)に見られる(写真A)のに対し、ILEIを
多量にもつモデルマウスの脳ではAβ沈着が明らかに少なくなっている(写真B)。
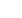
Y型迷路による記憶テストの結果
(グラフC)では、モデルマウスに記
憶力低下がみられるのに対し、ILEI
を多量にもつよう操作したモデル
マウスは健常マウスやILEIを多く
もつマウスと同じレベルの記憶力
を示し、記憶障害が抑えられてい
ることがわかる。
健常マウス ILEI
マウス
アルツハイマー病モデル
マウス アルツハイマー病モデル
ILEI
マウス
フッ素MR画像法という最先端の技術を駆使し、アルツハイマー
病MR画像診断薬の開発研究を行っています。これまでに、230種
類以上の化合物をスクリーニングし、有望な新規化合物34個を特
許出願しました。なかでも、Shiga-Y5は先行薬の10倍以上の強い
フッ素NMR信号を出し、アルツハイマー病モデルマウスで老人斑
の画像化に成功しました。また、Shiga-Y5は認知症の治療効果を
もつことも見いだしています。Shiga-Y5は2015年2月に日本およ
び米国の特許を取得しました。
We have developed a novel
19
fluorine (
19
F)-containing curcumin
derivative, named Shiga-Y5, as a potential imaging agent for
19
F-MRI.
Using Shiga-Y5, we have successfully obtained amyloid imaging in
the brain of a transgenic mouse model of AD. When AD model mice
were fed a chow diet that contained Shiga-Y5 for 6 months, the
mice improved memory impairment and reduced insoluble Aβ42 in
the brain. The results indicate that Shiga-Y5 is a potential diagnostic
and therapeutic agent for AD.
(Yanagisawa D et al., Neurobiol Aging 36: 201-210, 2015)
●神経難病に関する分子イメージング
Molecular Imaging of Neurological Diseases
神経難病研究
Research on Neurodegenerative Diseases
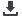
Shiga-Y5とShiga-X22の構造式
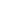
H-MRIは脳の構造をみるプロトンMR画像、F-MRIは老人斑をみるフッ素MR
画像。アルツハイマー病モデルマウスでは、フッ素画像(F-MRI)で老人斑を示
す黄色から赤色の画像が得られる。
Shiga-Y5とShiga-X22による老人斑の画像化試験
Research Activities
研究活動
第一部
17
第一部 滋賀医科大学の特色ある取り組み